Introduction. Autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targeting CD19 is an effective treatment for relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL). Real-world studies have reported improved outcomes in terms of safety and efficacy in comparison with pivotal trials. These differences have been associated to a learning curve in patient selection and adverse event control, but this hypothesis has not been proven. The aim of this study was to analyze patient selection and CAR T-cell management across different time periods and assess its impact on treatment outcomes
Methods. This retrospective analysis included all consecutive LBCL patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy (axicabtagene-ciloleucel [axi-cel] and tisagenlecleucel) in the third line setting from approval in 2019 to 2023 and reported in the Spanish Registry. Patients were categorized in 3 consecutive time periods of 18 months each according to infusion date. Baseline characteristics, manufacturing times and production failures as well as efficacy and safety outcomes were compared across periods. An additional safety and efficacy analysis was conducted in patients receiving axi-cel.
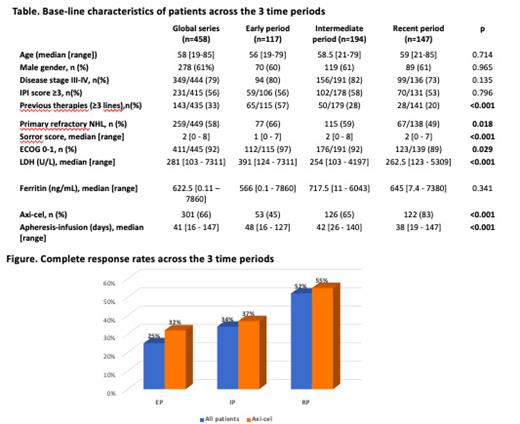
Results. The study included 458 patients: 117 (26%), 194 (42%) and 147 (32%) in the early (EP) (January 2019-June 2020), intermediate (IP) (July 2020-December 2021) and recent period (RP) (January 2022-June 2023), respectively. In terms of patient profile, baseline characteristics evolved overtime as patients in the RP had received less number of prior therapies, had less primary refractory disease, less bulky disease and had lower LDH at lymphodepletion. On the contrary, the RP had more patients with ECOG performance status ³2 and higher comorbidity burden. Regarding the product, the use of axi-cel increased overtime, from 45% in the EP to 83% in the RP (Table).
The time from apheresis to infusion improved overtime, moving from 48 days in the EP to 38 days in the RP. Manufacturing failures (5%) and use of bridging therapy (81%) remained stable overtime.
Regarding efficacy, overall (complete) response rates improved overtime (from 66% [25%] in the EP to 78% [52%] in the RP [p<0.001], respectively). Median PFS and OS for the whole cohort were 3.9 months (95% CI 3.23-5.83) and 18.5 months (95% CI 13.53 - 27.67) without differences across periods. In terms of toxicity, patients in the RP had more grade > or = 3 CRS and ICANS, received more tocilizumab and corticosteroids and required more ICU admission compared with the EP. These results were driven by the higher use of axi-cel in the RP.
When focusing exclusively on axi-cel patients (n=301), the CR rate also improved overtime (32% in the EP; 37% in the IP and 55% in the RP, p=0.016) (Figure) while median PFS (6.63 months, 95%CI 3.90 - 11.43) and OS (25.73 months, 95%CI 18.57 - NA) remained stable. In the multivariable analysis, ECOG PS > 1 (HR 2.68, 95% CI 1.35-5.09, p=0.005) and LDH ³ 500 UI/L (HR 1.54, 95% CI 1.02-2.31, p=0.04) but not treatment period were associated with a shorter PFS. In terms of toxicity, the time to CRS onset (median of 3 vs. 1 days, p=0.001) and ICANS (median of 8 vs. 6 days, p=0.06) was later in the EP compared with the RP. The incidence of grade > or = 3 CRS and ICANS (ranging from 10% to 7% and 36% to 41%, respectively), the use of tocilizumab, corticosteroids, and anakinra as well as ICU admission rate and 12-month non-relapse mortality (2% vs 5%) remained stable across periods.
Conclusion. The criteria for selecting patients for CAR T-cell therapy have evolved overtime towards a less aggressive disease profile and allowing less fit patients for therapy in recent times. Patients treated in the RP were more likely to respond to these therapies but this did not translate into prolonged survival or an improved safety profile.
Disclosures
Iacoboni:Miltenyi: Consultancy, Honoraria; Autolus: Consultancy; Abbvie: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria. Reguera:AMGEN: Speakers Bureau; KITE: Speakers Bureau; BMS: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Kwon:Jazz: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Speakers Bureau; Kite-Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Lopez Corral:Novartis: Honoraria, Other: travel support; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: travel support; Gilead Sciences: Honoraria, Other: travel support. Ortiz-Maldonado:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Miltenyi Biomedicine: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy; Celgene BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy. Mussetti:Gilead: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; BMS, Jazz Pharaceuticals: Consultancy. Martin Garcia-Sancho:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy, Honoraria; Clinigen: Consultancy; Eusa Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead / Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria; Lilly: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; ADC Therapeutics America: Consultancy, Honoraria; Miltenyi: Consultancy, Honoraria; Ideogen: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, BMS / Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Novartis, Gilead / Kite, Incyte, Lilly, ADC Therapeutics America, Miltenyi, Ideogen, Abbvie, Sobi: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, BMS/Celgene, Janssen, Gilead/Kite, Takeda, Eusa Pharma, Abbvie: Honoraria. Bastos-Oreiro:Incyte, Kite: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Kite, SEHH, AMHH: Research Funding; SEHH, AMHH: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS, Kite, Novartis, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Incyte, Abbvie: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Gregorio Maranon Hospital: Current Employment, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Carpio:BMS: Consultancy; Gilead: Honoraria; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria. Barba:Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pierre-Fabre: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Nektar: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Miltenyi Biotech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Allogene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz Pharmaceutical: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal